3D Scanners
Showing all 7 results
-
Request a Quote Request a Quote
-
-
-
-
Showing all 7 results
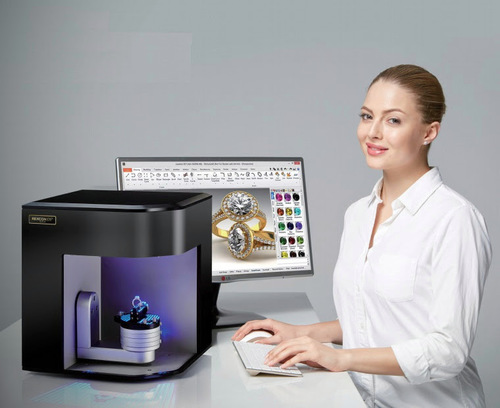
Introduction to 3D Scanner
3D scanners are devices that capture the shape and geometry of physical objects to create 3D models. There are several types of 3D scanners available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are some examples of the different types of 3D scanners:
- Structured light scanners: These scanners project a pattern of light onto an object and use cameras to capture the distortion of the pattern. By analyzing the distortion, the scanner can calculate the 3D shape of the object.
- Time-of-flight scanners: These scanners use a laser to measure the time it takes for the laser light to bounce back from an object. By measuring the time of flight, the scanner can calculate the distance to the object and create a 3D model.
- Laser triangulation scanners: These scanners use a laser to project a line onto an object, and a camera captures the position of the line as it moves across the object. By triangulating the position of the laser line, the scanner can create a 3D model.
- Photogrammetry scanners: These scanners use a series of photographs taken from different angles to create a 3D model. The photographs are analyzed using specialized software that can calculate the position and orientation of the camera, allowing for the creation of a 3D model.
3D scanners have many applications in fields such as manufacturing, engineering, and art. They can be used to create accurate models of objects for use in product design, reverse engineering, and quality control. They are also used in medicine to create 3D models of patients’ anatomy for surgical planning and education. Additionally, 3D scanners are used in archaeology and cultural heritage preservation to create accurate digital models of historical artifacts and monuments.