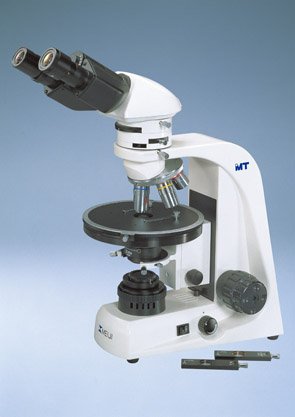
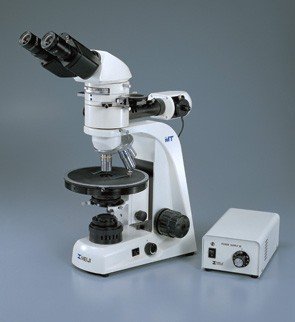
Polarizing / Polarising Microscopes
Showing 1–9 of 22 results
-
-
-
$USD 6,143.00 Add to cart
-
-
-
$USD 5,535.00 Add to cart
-
Showing 1–9 of 22 results
Polarising / Polarizing Microscopes
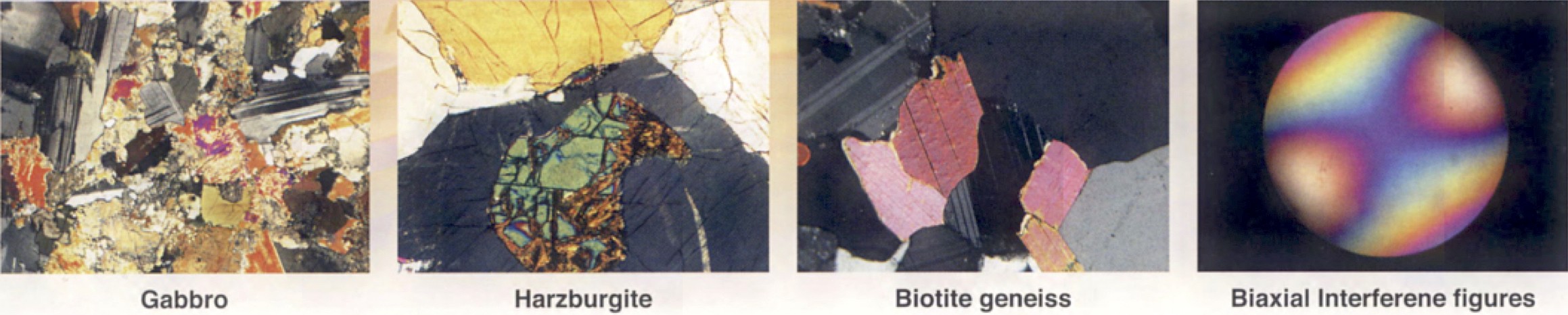
A polarising microscope is a type of microscope that uses polarised light to examine the properties of materials such as crystals, fibers, and thin films. It consists of a light source, polarising filters, and a polarising lens that can be rotated to change the orientation of the polarisation.
When light passes through a polarising filter, it becomes polarised, meaning that the waves of light oscillate in a single plane. When this polarised light passes through a sample, it interacts with the material’s properties, causing changes in the polarisation direction and intensity. By analyzing the way that the polarised light interacts with the sample, a polarising microscope can provide information about the material’s crystal structure, optical properties, and other characteristics.
Polarising microscopes are commonly used in geology, mineralogy, materials science, and other fields where the properties of crystalline materials are of interest. They can be used to identify minerals and crystals, determine the composition of materials, and study the behavior of materials under stress or other conditions.
In addition to standard polarising microscopes, there are also specialized types of polarising microscopes such as transmitted light polarising microscopes, reflected light polarising microscopes, and polarising microscopes with imaging capabilities.
Polarising microscopes are offered with reflected (incident) light only, transmitted light only (for transparent samples), or with both reflected & transmitted lights.
All polarising microscopes come with brightfield (BF) imaging and polarized imaging capability. There are some models that support brightfield and darkfield imaging.
Most of polarizing microscopes come in upright mode. If you need to have either an inverted microscope with polarization rather than upright, or need a microscope with all imaging capabilities (brightfield, darkfield, polarizing, DIC Nomarsky, or fluorescence), then please look at our inverted metallurgical microscopes such as BMI600, or upright metallurgical microscopes such as BMU500DIC.
Read more on Polarizing Microscopy Imaging (Basics & Applications)
A polarizing microscope, also known as a polarized light microscope, is a type of microscope that uses polarized light to study the properties of materials. The microscope consists of a light source, a polarizer, a sample stage, an analyzer, and an eyepiece.
Polarized light is light in which the waves oscillate in a single plane, rather than in all directions. This light is produced by passing unpolarized light through a polarizer, which is a filter that allows only waves oscillating in a particular plane to pass through.
In a polarizing microscope, polarized light is directed through the sample on the stage, which interacts with the material’s properties, causing changes in the polarisation direction and intensity. The analyzer, which is another polarizer that can be rotated, is placed above the sample stage and blocks out all polarized light that is not aligned with its axis of polarization. By rotating the analyzer, different properties of the sample can be observed and analyzed.
Polarizing microscopes are commonly used in materials science, geology, and other fields where the properties of crystals, fibers, and other materials are of interest. They can be used to identify minerals, study the behavior of materials under stress or other conditions, and determine the composition of materials.
Polarizing microscopes can also be used in conjunction with other techniques, such as fluorescence, to provide additional information about the properties of the sample.